Can Orthotic Insoles Treat Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
Updated January 25, 2024.

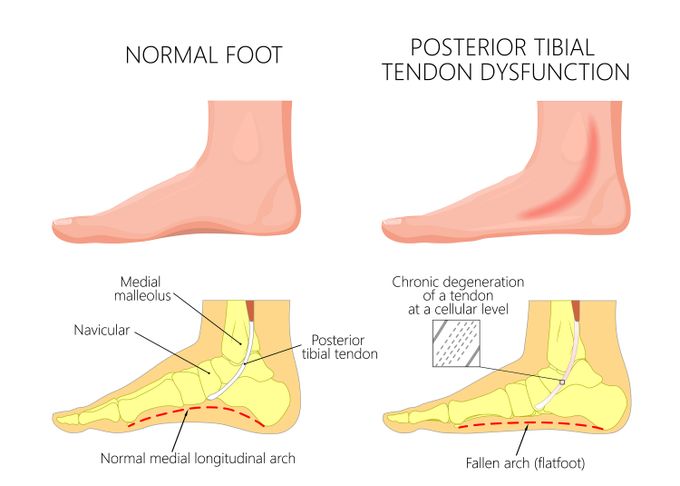
Posterior tibial tendonitis, also called posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD), is a condition that causes inflammation of the tendons on the inner side or medial part of the ankle (posterior tibial tendon). This article will detail the symptoms and causes of PTTD, how to fix PTTD, and the effectiveness of using orthotic insoles.
Symptoms of PTTD
The most common symptoms of PTTD are:
- Pain located on the inner side of the ankle that worsens with activity.
- Inflamed and swollen posterior tibial tendon.
- Restriction in ankle joint movements.
- Balance and stability issues while standing and walking.
- Unsteady gait patterns.
PTTD happens in 4-5 stages depending upon the severity of the condition and the individual case. Higher stages imply a severe condition with either a fixed or a flexible foot deformity.
Causes of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
PTTD usually occurs as a result of any or all of the following:
- Overuse by repetitive activities and inadequate rest.
- A recent ankle sprain.
- Being obese or overweight.
- Laxity of the ligaments supporting the ankle joints.
- Hypertension.
Typically, you are more at risk for PTTD if you:
- Have flat feet.
- Are a young athlete playing high-impact sports.
- Are elderly (especially true for idle women).
Additionally, PTTD can be aggravated by several activities, such as walking, running, hiking, and stair climbing.
What Is the Best Treatment for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
The good news is that PTTD can be treated. The treatment option depends on its severity. In most patients, the condition is mild, and symptoms will resolve with conservative and non-surgical management. This includes a mix of rest, ice, pharmacological management, immobilization, orthotics, and physiotherapy. In more severe cases, surgical repair may be necessary.
It is important to note that, even with early intervention, pain may last longer than 12 weeks. However, for patients who have developed chronic pain before intervention starts, pain may last for another 6 months before resolving. Here is what each treatment approach entails:
Medical Management
Your general physician may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to help control the pain and inflammation. When taken at least 30 mins before exercise, they make exercise more bearable by limiting inflammation. However, once you've used NSAIDs for up to a month, consider revisiting your physician.
Physical Therapy
Going under a complete rehabilitation program with your physical therapist is essential to recovering from PTTD. The rehabilitation is done according to the stage of the condition and can be any of the following:
- Ice Using ice in the acute stage can help control inflammation.
- Activity modification To give the leg some much-needed rest, it may be necessary to decrease some activities. Total sedentary behavior is usually unachievable for most individuals, and so, at the very least, you should avoid high-impact exercises like jogging and running. For example, biking, elliptical machines, and swimming do not put a large impact load on the foot and can be tolerated by most patients.
- Implementation of an exercise program Usually, this includes mobility, stretching, and strengthening exercises for the posterior tibial tendon.
- Immobilization Immobilizing the foot in a walking cast or boot and avoiding weight-bearing activities allows the tendon healing time in the acute stage. This must be used with caution as it can cause muscles of the foot to atrophy. Often, this option is used only if other conservative methods have not yielded results.
- Massage Gentle self-massage using the pad of your thumb can relieve pain and relax the structures around the medial ankle.
Proper Footwear
While over-the-counter pain-relief insoles will be enough in someone with a mild change in foot shape, a custom orthotic is necessary where there is a severe deformity. Custom orthotics are specifically designed to improve arch support and foot function for your unique feet.
Furthermore, wearing the appropriate shoe is still often underrated as a means of managing PTTD; yet it works. Wearing the right shoes will help maintain proper foot alignment and prevent injury. This invariably helps to improve the symptoms of posterior tibial tendonitis.
Surgical Management
When conservative management fails to bring pain relief in severe conditions, surgical treatment is the next option for treating fixed or flexible foot deformities. The type of surgery will depend on the location of tendonitis and the severity of the damage. Common procedures include lengthening of the Achilles tendon, tenosynovectomy, tendon transfer, osteotomy, and fusion.
How Can Orthotic Insoles Help PTTD?
The aim of using orthotics for posterior tibial tendonitis is to decrease the patient's pain, speed up activity and function, maintain the foot and ankle in a neutral position, and forestall the development of deformity.
To achieve this, orthotic insoles are custom-fitted to provide extra cushioning to the arches of feet and the metatarsals. These play important roles in optimal weight distribution and protect the ball of the foot from more damage.
In addition, these insoles provide support to the medial arch (also called flat feet) and the inner aspect of your foot. Consequently, the foot is kept in an optimum position to allow proper functioning. As long as it is functioning correctly, you can expect to feel relief, and your daily activities can return to normal.
» Ready to purchase some orthotics? Take a look at our complete collection of Custom Orthotics
How Effective Are Orthotic Insoles for PTTD?
Research has found that:
Additional research surmised that:
This means that posterior tibial tendonitis orthotics play a vital role in the treatment of PTTD along with physiotherapy management. They will assist in optimizing foot loading, supporting and maintaining the arch, and improving the foot biomechanics.
Proper functioning of human lower limbs is highly dependent on the biomechanics of the feet, which is altered due to a collapse of the medial arch and leads to excessive pronation of the feet (ankles that roll inward).
Few things are as effective in maintaining the biomechanics of the foot as custom-made insoles. They will help in maintaining and helping the collapsed arch improve with time. The orthotics themselves require very supportive and spacious footwear to both fit in and function at their best. Good quality athletic shoes, hiking boots, or similar are ideal for achieving the best results possible.
» Alleviate pain and discomfort with the best insoles for posterior tibial tendonitis
Are Custom Orthotics Worth It for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
In conclusion, as illustrated above, custom orthotics are an essential adjunct to achieve a complete recovery from posterior tibial tendonitis. They allow for ultimate support by applying the correct force on the feet, reducing the load placed on the tendons. Essentially, yes, custom orthotics are worth it for posterior tibial tendonitis.